Off-grid solar systems, powered by captured sunlight and stored in batteries, offer energy independence from utility grids. These sustainable solutions, made affordable by tech advancements, include high-efficiency panels, robust batteries, inverters, and meticulous installation for reliable electricity generation and storage. Strategic design, regular maintenance, and efficient usage maximize sun exposure, optimize performance, and ensure a continuous power supply. Solar Energy integration enhances self-sufficiency while reducing carbon footprints.
“Unleash energy independence with off-grid solar solutions! This comprehensive guide explores your path to sustainable power. Discover how off-grid solar systems harness the sun’s potential, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional energy sources. From understanding system dynamics and reaping environmental benefits to designing tailored solutions and maintenance tips, this article equips you to maximize solar energy potential. Embrace self-reliance with these essential insights into solar energy independence.”
- Understanding Off-Grid Solar Systems: How They Work and Their Benefits
- Components of a Successful Off-Grid Solar Installation
- Designing an Off-Grid Solar Solution for Your Home or Property
- Maintaining and Maximizing Your Solar Energy Independence
Understanding Off-Grid Solar Systems: How They Work and Their Benefits
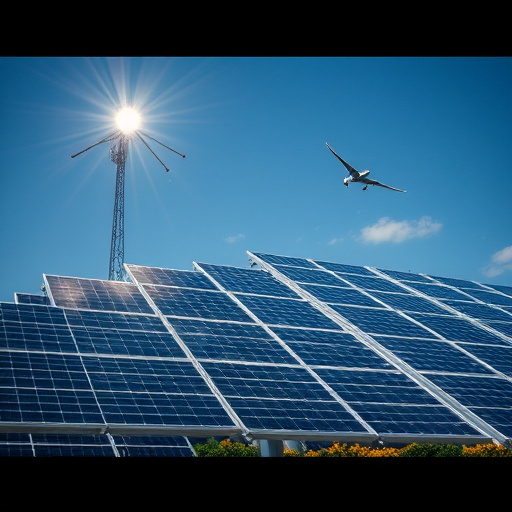

Off-grid solar systems harness the power of the sun and convert it into electricity, enabling energy independence for homes and businesses. These systems differ from on-grid setups by not relying on the local power grid. Instead, they use solar panels to capture sunlight, which is then stored in batteries for later use. This stored energy becomes the primary source of electricity, eliminating dependence on traditional power utilities.
The benefits of off-grid solar solutions are numerous. They offer a reliable and sustainable energy source, particularly in remote areas with limited access to the grid. Once installed, these systems provide long-term savings by reducing or eliminating utility bills. Additionally, they contribute to environmental conservation by decreasing carbon footprints associated with conventional energy generation. With advancements in technology, off-grid solar has become more efficient and affordable, making it a viable option for those seeking energy independence and sustainability.
Components of a Successful Off-Grid Solar Installation
A successful off-grid solar installation comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in harnessing and storing solar energy effectively. Firstly, high-efficiency solar panels are essential to maximize electricity generation from sunlight. These panels should be of premium quality, designed for rugged conditions, and optimized for the local climate and radiation levels.
Complementing the solar panels is a robust battery system that stores the captured energy for use during periods of low or no sunlight. Deep-cycle batteries, typically lead-acid or lithium models, ensure a reliable power source for essential appliances and systems. Additionally, a well-designed inverter is crucial to convert the stored DC energy into AC power, enabling compatibility with standard household electrical systems. Proper wiring, mounting, and grounding are also critical aspects that guarantee safe and efficient operation of the off-grid solar installation.
Designing an Off-Grid Solar Solution for Your Home or Property

Designing an off-grid solar solution involves careful planning and consideration of your energy needs, available space, and budget. The first step is to assess how much solar energy your property can generate by evaluating its sun exposure, shading, and physical size. It’s crucial to understand your daily and seasonal energy consumption patterns to accurately determine the required number of solar panels and supporting battery storage capacity.
Next, integrating these components seamlessly requires a well-thought-out layout. This might involve positioning panels at optimal angles and orientations, selecting suitable mounting systems, and planning for efficient wiring and inverter placement. Many homeowners opt for ground-mounted arrays for larger installations, while others choose roof-mounted options for easier maintenance. Regardless of the setup, the goal is to maximize solar exposure while ensuring a robust and reliable off-grid energy system.
Maintaining and Maximizing Your Solar Energy Independence
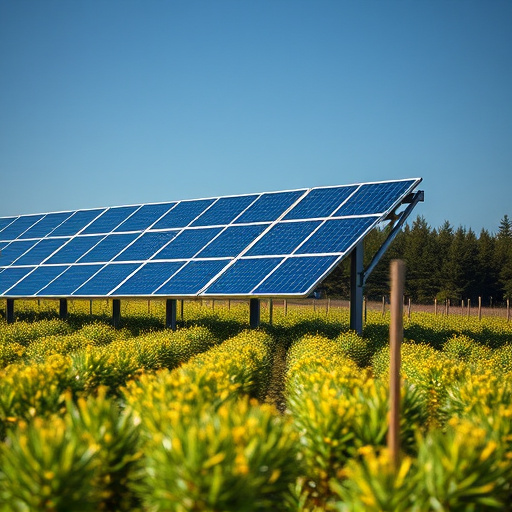

Maintaining and maximizing your solar energy independence involves a combination of smart design, regular upkeep, and efficient usage. Start by ensuring your solar panels are installed in areas with optimal sunlight exposure throughout the year. Regular cleaning and maintenance, including trimming nearby vegetation, can significantly boost energy production. Invest in high-quality components and consider using microinverters for each panel to maximize efficiency and simplify troubleshooting.
Monitor your system’s performance using digital tools that track energy generation and consumption. This data allows you to identify any issues or inefficiencies early on. Adjust your energy usage patterns accordingly, prioritizing energy-saving appliances and lighting during peak sunlight hours. By integrating smart thermostats and energy storage solutions like batteries, you can further enhance your energy independence, ensuring a reliable and sustainable power supply for your home or business.
Off-grid solar solutions offer a path towards energy independence, empowering individuals to break free from traditional power grids. By harnessing the infinite resource of sunlight, these systems provide clean, sustainable energy for homes and properties. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, as outlined in this article, you can enjoy the numerous benefits of solar energy, including reduced utility bills, environmental impact mitigation, and resilience during power outages. Embracing off-grid solar is a step towards a more sustainable future, where individuals take control of their energy consumption.
